Legal visit exposes apparent abuse in Immigration detention centre
May 20th, 2015 | Detention, Government, Immigration, Legal, Rejection, VF Opinion | Comment
Vision First fearlessly reports on incidents that place under the spotlight practices adopted by various Government bodies which include the Director of Immigration, Security Bureau, Social Welfare Department and Hospital Authority.
Examples are asylum policies resulting in an effective zero percent acceptance rate, welfare failures, institutional discrimination and abuses of power by those in authority. It is unfortunate that enormous and entrenched distrust continues to widen between refugees and Government authorities, with officials often failing in their duties prescribed by law.
Government propaganda and uninformed media reports often depict refugees as abusers of the asylum process accusing them of exploiting the system for personal gain. Such generalisation is simply untrue for asylum seekers who fled torture, ill-treatment, death threats and persecution to seek protection from Hong Kong’s Government.
It is increasingly clear that the secretive walls of the Director of Immigration’s Castle Peak Bay Immigration Centre (CIC) conceal apparent unlawful conduct. On 6 May 2015, Vision First arranged a visit to CIC to provide free legal advice to refugees in relation to asylum claims, the legality of such procedures, conditions and legality of detention and to secure their release from arbitrary deprivation of their liberty
The pro bono legal team comprising Barristers Mark Sutherland and Robert Tibbo, together with their instructing solicitors and interpreters, paid a visit to CIC. This is what transpired. One refugee from Africa had reportedly been detained in CIC for over three and a half months whilst the assessment of his “first tier” non-refoulement claims was underway with all the interviews so far being conducted within CIC. His next interview was due to take place the following day, 7 May 2015.
Another refugee from Africa had been reportedly detained for over a month and only that morning had been handed a set of blank Supplementary Claim Forms by The Duty Lawyer Service (DLS). This was presumably prompted by the prior lodgement of a non-refoulement claim. The assessment of this refugee’s claim had not even started and a lawyer not yet assigned to him by DLS.
A further refugee from South Asia reported that he had attempted to argue his own Appeal without a lawyer and had experienced a detention period of seven months.
Troubled by his findings of lengthy periods of detention, Barrister Mark Sutherland asked to see the supervising Immigration officer. During the course of an hour, three Immigration officers of differing levels of seniority appeared but could not shed any light on the seemingly unlawful detention of the refugees.
Finally, the Superintendent of CIC, a Mr. W.S. Kwong, the highest ranking Immigration officer responsible for CIC attended and agreed to a meeting with the pro bono legal team during which serious concerns were expressed as to the legality of the detention of the refugees. Sutherland asked Mr. Kwong: “Are you aware of the Ghulam Rbani case?” Mr. Kwong replied words to the following effect: “I have never heard of it. It’s not my department.”
Superintendent Kwong was unaware of this landmark and legally binding decision of the Court of Final Appeal case “Ghulam Rbani vs. Secretary for Justice” (FACV 15/2013), wherein it states:-
“Once it became clear that the CAT claim had to run its course, it would have been obvious that no decision to make a removal order could have been arrived at within the maximum period of detention permitted under section 32. Applying the 3rd Hardial Singh principle, steps should then have been taken without delay to effect the appellant’s release.”
Put simply, if an asylum seeker has filed a claim for non-refoulement protection, he cannot lawfully be detained and must be released forthwith.
Vision First is of the view that the Director of Immigration, Mr. K.K. Chan, should call for an immediate review of the detention status of each and every inmate currently held at CIC. Sutherland invited Superintendent Kwong to see that such a review was undertaken as a matter of priority. The result is awaited.
Based on this legal visit, Vision First is satisfied that there is sufficient evidence to merit an independent investigation of the apparent disregard by the Hong Kong Government of the principles enunciated by the Court of Final Appeal in Ghulam Rbani. We shall leave it to our readers to draw their own conclusions.
Pro bono legal team enters CIC to secure release of refugees
May 8th, 2015 | Detention, Immigration, Legal, Rejection | Comment
May 6th of 2015 is likely to be a day many refugees detained by the Director of Immigration at the Castle Peak Bay Immigration Centre (CIC) will not easily forget. The Refugee Union had taken instructions from over 30 detainees to arrange a legal visit by a pro bono legal team to advise them on their asylum claims, the legality of the asylum claim procedures, conditions and legality of detention and to secure their release. Since a group visit by a pro bono legal team had not occurred for some time, the refugees were hopeful whilst not knowing what to expect.
The legal team comprised Barristers Mr. Mark Sutherland and Mr. Robert Tibbo, both non-executive directors of Vision First, who scheduled valuable time to provide free legal advice to the detainees, some of whom have indeed been unlawfully detained. Counsel were instructed by solicitors Mr. Tam Kam Tong and Mr. Chris Lucas respectively, who were supported by interpreters – everyone acting on a pro bono basis.
The Director of Immigration had been notified of the legal visit to a number of refugees for the purposes of assessing “current detention at CIC and to advise on possible claims under Article 2 of the Bill of Rights Ordinance.” The legal visit was also to focus on the procedure for judicial review. Led by Superintendent W.S. Kwong, Immigration officers and staff were helpful throughout the particularly busy day.
Sutherland remarked, “There are several refugees who have been locked up since they arrived despite having lodged claims for asylum. In some cases, their interviews haven’t even started. This is clearly a prima facie case of unlawful detention and immediate release has been requested.” Tibbo added, “One youth from South Asian was so traumatized by his treatment by the Director of Immigration at CIC that he gave up and withdraw his non-refoulement protection claim. They are being warehoused in a similar way to Australian off-shore detention camps.”
A sense of encouragement grew among refugees from morning till afternoon. The initial uncertainty about the magnitude of events lifted as the first clients returned to the common rooms to share their experiences. Tibbo observed, “It was like a fire was spreading inside CIC. The refugees knew their lawyers were there and they might be released soon. Clients were coming in to the meeting rooms and everyone was fired up and happy – there was a resurgence of hope that could been seen in their eyes and faces.”
After lunch, while inside CIC, Sutherland came across quite per chance two visitors who turned out to be the Justices of the Peace (JPs) assigned to inspect CIC. JPs are the only independent professionals granted unrestricted access to the centre, where they may speak to detainees without appointment and request copies of detention files. The two gentlemen were clearly alarmed by the grave concerns expressed by Counsel which had arisen out of the legal visit. The JPs kindly held two meetings with the legal team on the same day. They requested a full report of the findings. Interestingly, Vision First was in the process of preparing to make contact with the JP’s Office to seek assistance in relation to detention concerns. Sutherland has since conveyed the matter in writing to the JPs in question.
By 5 p.m., the legal team requested the Director of Immigration to immediately release 6 (six) refugees who have been arbitrarily and unlawfully detained by the Director of Immigration. Their release is expected imminently. It is noteworthy that several refugees on the original list had already been released from detention prior to the legal visit.
It is believed that the legal team’s effort will have an impact on the way certain matters are carried out behind the secretive walls of Immigration detention. It now appears clear that refugees are being unlawfully detained in CIC whist they have outstanding non-refoulement claims.
In reality more than occasional pro bono efforts are needed to ensure high standards of fairness in Immigration detention and to hold the Director of Immigration, Mr. K.K. Chan to account. There should be a panel of lawyers assigned either by The Director of Legal Aid and/or The Duty Lawyer Service to meet this crucial need. These lawyers should be on hand at CIC to offer on the spot legal advice to detainees, regarding their detention and with the authority to launch habeas corpus proceedings, if necessary.
The present lacuna in the provision of free legal advice regarding detention plays into the hands of the Director of Immigration and militates towards longer periods of unchecked, unlawful detention.

Why is Hong Kong hostile to refugees?
May 6th, 2015 | Detention, Immigration, Legal, Rejection, VF Opinion | Comment
It was hard to answer the question of a visitor to Vision First who sought to understand the caustic environment navigated by refugees with a slim chance of securing protection in an indifferent city. Ironically, Hong Kong has long had a history of welcoming refugees (1.5 million between the 1930s and 1970s), but its sympathy and support of persecuted foreigners dwindled regrettably as residents became richer.
The government mantra is well rehearsed, “Non-refoulement claims lodged under the USM are not asylum claims. The Refugee Convention and its 1967 Protocol have never applied to Hong Kong. The Government maintains a firm policy of not granting asylum to or determining the refugee status of anyone. Our policy objective is to screen … and to remove rejected claimants from Hong Kong as soon as possible. Lodging a claim does not change the fact that non-refoulement claimants are illegal immigrants or overstayers.”
The results of such a policy appear skewed towards removal. Between 2009 and 2014, Immigration screened 5581 claims and substantiated just 25. It is noteworthy that in 6 years Immigration failed to grant protection to a single asylum seeker among 2166 Pakistani, 1760 Indians and 1237 Bangladeshi. Hong Kong has never protected a claimant from these countries. By contrast, in 2013 Australian protection grants produced very different results: Pakistani 80.4%, Indians 6.3% and Bangladeshi 42.7% at first instance (p. 20). Astonishing it is that Pakistani scored 94.9% including appeals (p. 30). How does it compare to Hong Kong’s achievements?
Despite profuse assurances to the contrary, it appears that Hong Kong Government has abdicated its obligation to protect refugees and has instead prioritized rejection and removal. An elaborate performance by 480 lawyers ‘who have received specialised training’ has done little to improve the effective zero percent acceptance rate. To the contrary, the authorities are focused on cost-cutting to reduce the $644 million spent on claimants, including legal aid up 86% last year.
Stringent immigration control and deterrent welfare were ingeniously deployed to deter asylum seekers from remaining in Hong Kong, but their number doubled in 2014 to 9618, reflecting worrying global trends. Immigration is presumably feeling the pressure and this year plans to determine 2000 claims, which might fail to reduce the total ‘with new claims coming in at more than 300 per month since early 2014.’
In an obfuscated environment of rejection and expediency, is it possible that some refugees might be removed or deported to their country of origin at a risk of life and limb? It is hard to make factual assessments, as the Castle Peak Bay Immigration Centre (CIC) remains off-limits to rights advocates and detainees may only be visited by appointed lawyers. Refugees denied release on recognizance are unlikely to enjoy adequate legal advice, or second opinions on their claims.
In this potential black hole, can Immigration be trusted to adhere scrupulously to high standards of fairness, respect fundamental refugee rights and assess claims in a non-adversarial manner as required by law? Acting on a pro bono basis, barristers Robert Tibbo and Mark Sutherland, non-executive directors of Vision First, visited CIC on 6 May 2015 to take instructions from 24 detainees who sought the assistance of the Refugee Union against imminent removal orders. It was reported that 5 had already ‘left from Hong Kong International airport’ with no further details.

Security Bureau update on the Unified Screening Mechanism
Apr 30th, 2015 | Crime, Detention, Government, Immigration, Legal | Comment
Hong Kong requires a legal board in Castle Peak Bay Immigration Centre
Apr 30th, 2015 | Detention, Immigration, Legal, Refugee Community | Comment
A year before the Unified Screening Mechanism was launched in March 2014, Vision First campaigned vigorously against Immigration Department’s apparently biased conduct and ostensible refusal to entertain CIDTP claims during the torture claim screening process. It is alarming that presently the problem is being repeated in relation to “Right to Life Claims.”
The rule of law in Hong Kong requires that every asylum claim be assessed with “anxious scrutiny and high standards of fairness” before Immigration exercises its statutory power of removal or deportation (CFA Prabakar case, Jun 2004) . This gives rise to an obligation to recognize the right not to be subject to torture, CIDTP and persecution for persons having no right to enter Hong Kong, including refugees detained in Castle Peak Bay Immigration Centre (CIC) – some who have never been released on recognizance.
Backed by reports from claimants detained for prolonged periods, Vision First is concerned by the secretive nature of detention at CIC. The availability of publicly funded lawyers and interpreters at interviews in CIC is not a guarantee of high standards of fairness when refugees are denied second opinions and there is no legal board to offer advice to those in need.
A Middle Eastern refugee was detained over 8 months and resisted several attempts at removal. He reports, “Immigration refused to believe me. They forced me to the airport but I resisted. I knew my rights and demanded to be released to prove my case. Others who didn’t speak English were not as lucky as me.”
A refugee from India had his case rejected as he languished for 10 months in CIC. He recalls, “My lawyer told me to drop my claim and leave Hong Kong. He refused to help me with the appeal. I thought he was serving the interests of Immigration.”
In April 2015, Vision First met with the Hong Kong Bar Association to raise concerns about the respect of fundamental refugee rights in CIC detention. Circumstantial evidence suggests that Immigration is arbitrarily denying applications for “Right to Life” protection in the centre. There is a widely held belief that the zero percent acceptance rate reflects a strategy to deny protection despite the potential risk of life and limb for those expelled from Hong Kong.
Detainees would be alarmed to know that between 2009 and 2014 Immigration rejected 99.54% of 5581 claims determined. It is doubtful that any one of the 25 substantiated claimants was recognized inside CIC and released with protected status. Immigration should report how many claimants from which countries are detained at the airport, screened in detention and removed without being released on recognizance. What assurances can be made that they were treated fairly?
Hong Kong urgently requires a legal board to independently advise claimants in Immigration detention and prisons, monitor the implementation of asylum practices and ensure that the Unified Screening Mechanism pays more than lip service to high standards of fairness. Until that day comes it is suspected that the screening system lacks credibility, not refugees.
A month has passed since Vision First wrote an open letter to Immigration raising a series of questions in connection with Right to Life claims. Disappointingly no substantive reply was received from the Director of Immigration. In early April the Refugee Union established a 24-hour helpline for CIC detainees who can only make two local phone calls a month. The union has been contacted by dozens of refugees who appealed for independent legal assistance with asylum claims and lamented the treatment they received away from the public eye.

True protection eludes a recognized refugee
Apr 29th, 2015 | Immigration, Medical, Personal Experiences, Rejection, VF Report | Comment
After five years of deep emotional and economic suffering in Hong Kong, on 15 January 2015 Ali was rushed to the hospital with pain in his chest. He recalls, “The medical officer informed me that one of my heart vessels is blocked. They (need to perform an) angioplasty to fix a stent in the blocked vain. But I have to pay 20,000 HK$ myself as the stent is not available from the hospital (free for refugees). I told him that due to my status, it is not possible for me to pay such a huge amount … ISS case worker and UNHCR said sorry that we do not have funds for that purpose.”
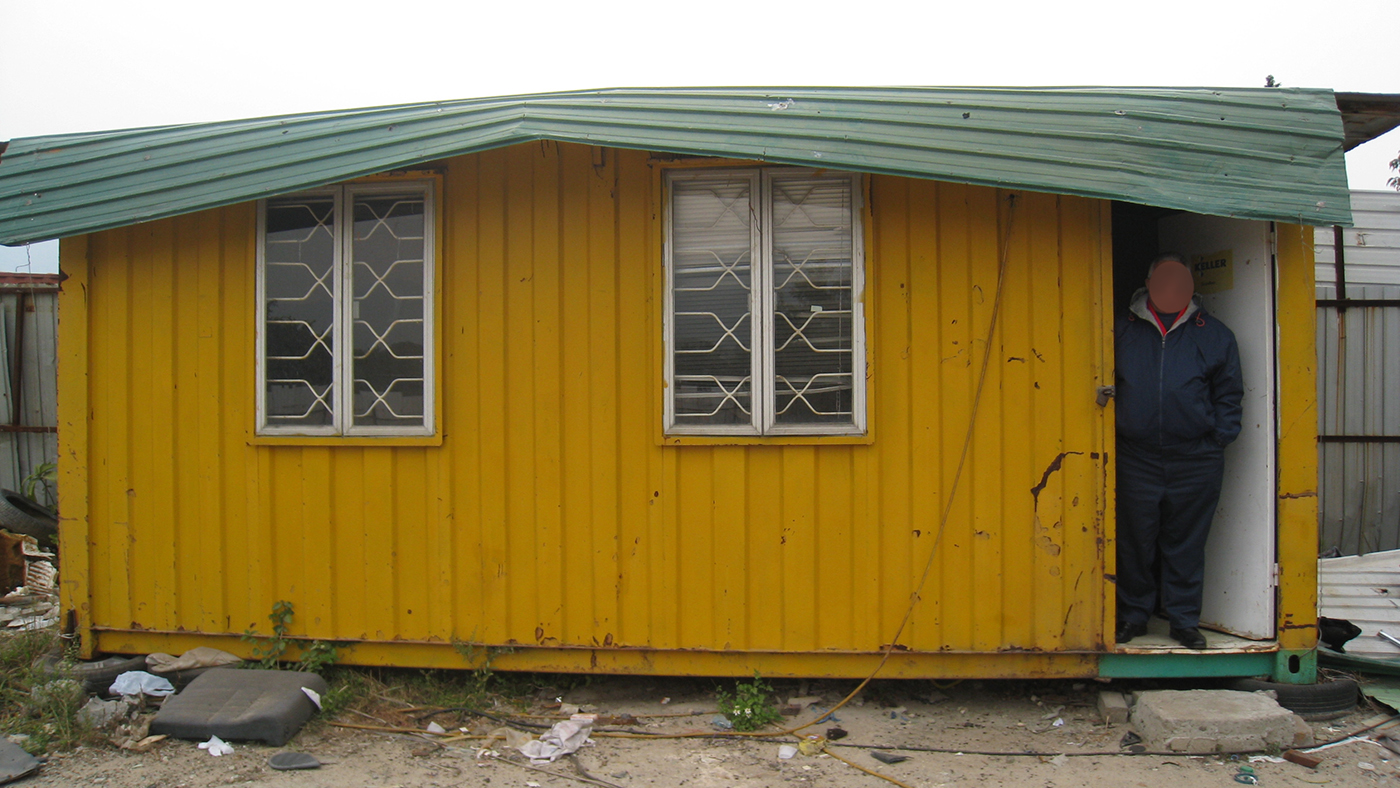
Who is Ali? Ali is a 62 year-old recognized refugee from Pakistan in Hong Kong since January 2010. He spent several winters freezing in a container abandoned in a Kam Tin recycling yard. In the summer his home became unbearably hot. Before rental deposits were introduced for refugees, Ali accepted such limited hospitality from residents offering temporary shelter. By living in a possible illegal work place, the Pakistani defied the common assumption that his countrymen abused asylum to work in Hong Kong.
For five years, Vision First followed closely Ali’s asylum experiences in our inhospitable city.
Ali feels betrayed by Hong Kong’s promises of protection, “In January 2010 I left my country, business, mother, wife, children, brothers, sisters, friends and relatives hoping that Hong Kong Government and UNHCR will appreciate our sacrifices in the war against terrorism by opening their hearts and help us in standing again on our feet. But all our expectations were ruined by the different functionaries of the government and UNHCR.”
In May 2011 the Immigration Department rejected Ali’s torture claim at appeal. He was stoically terse, “It is a childish decision!” The rejection by UNHCR in December 2012 was traumatizing, as it crushed his trust in the international agency. When Legal Aid rejected his application to judicially review his CAT rejection, the disheartened family man hit rock bottom. Sick and depressed, Ali seemed on the verge of giving up more than his bid for asylum. In those dark days, only family thoughts kept him going, “I have many burdens with my family. How can I help them? The whole family is looking to me. They are stuck. They want to know when they can come and join me.”
Conspiracists might be forgiven for speculating about the baffling backpedaling by UNHCR which unexpectedly confirmed his status as a refugee on 29 April 2014. It might not be a coincidence that Ali’s lawyers had reversed the Legal Aid decision and prepared a well-document, arguable case that might have forced Immigration to reconsider its decision. Ali suspects that the government put pressure on UNHCR to resolve his claim and stop legal proceedings.
At the time he was hospitalized, Ali was informed that since his condition had not reached a ‘life threatening state’, the hospital could not proceed with free surgery and he would have to pay for the stent himself. Five years in limbo without the right to work dilapidated Ali personal resources. Today he is truly destitute. ISS-HK referred him to SWD which unempathically stated that they would not pay until his condition deteriorated.
Let’s face it. Ali has been treated poorly from the day he arrived and was reduced to living in a shipping container for years. His family was displaced and fell from relative prosperity to grim poverty. Now Ali spends the days bedridden in a room that appears to be an illegal structure. He is afraid his heart will fail overnight. He hardly dares to walk outside for fear of collapsing in the street, which ironically might be the only chance he has to receive the necessary surgery.
Hospitals, ISS-HK and SWD kick away responsibility like a ball. Is it reasonable to ask a sick refugee to raise money himself to save his life despite being granted international protection? What meaning does the status of refugee carry for UNHCR, ISS-HK, SWD and the government? Who will be held accountable in a worst case scenario for such absurd conditions of institutional punitive confinement? Hong Kong should step up and honor Ali’s protection with the peace of mind and wellbeing it ought to entail.

A legal and moral obligation to increase welfare to realistic levels
Apr 23rd, 2015 | Housing, Immigration, VF Opinion, Welfare | Comment
Refugees in Hong Kong worry most about two issues: protection and welfare. Over the years the Immigration Department has done little to allay suspicions that the effective zero-percent acceptance rate is a poor assessment of the asylum community. Welfare issues are equally troubling with policies that deliberately entrap refugees below the poverty line without employment rights.
On a scale of importance, Vision First is primarily concerned about the failure of the Unified Screening Mechanism to generate protection. In the interest of accountability and transparency, Immigration ought to publish monthly results to inform interested parties about its accomplishments in the asylum sphere. This would undoubtedly better inform opinions.
After Hong Kong’s top court denied the right to work in February 2014 to mandated refugees and successful torture claimants, it became disappointingly clear that the authorities are years away from granting employment rights to asylum seekers condemned, by policy and design, to a protracted state of emotional and economic destitution with deterrence aims.
A combination of questionable policies force refugees to run the gauntlet between insufficient welfare and imprisonment for working illegally. Such arrangements strike offenders heavily with arrests and imprisonment that are hardly avoidable when money must be regularly raised to meet necessary expenses, such as rent surpluses, utilities, food and clothing.
Instigated by superficial media reporting, common perception assumes that refugees should receive less welfare than impoverished residents. This is shamefully reflected in the welfare disparity between citizens and refugees, despite the former being allowed to work and the latter jailed up to 22 months for breaking the law in a hostile, and arguably unjust environment.
On 22 April 2015, Vision First and the Refugee Union met with the Hon. Fernando Cheung Chiu-hung to strategize on increasing welfare levels that are unrealistically low (HK$ 1500 for rent and HK$ 1200 for food) and have fallen behind inflection, particularly in the rental market. A first batch of 300 complaint forms were submitted to the Legislative Council’s Redress System to trigger a discussion by the Panel on Welfare that advises the government on such matters.
Questions will be raised about the adequacy of the current assistance which fail to meet the basic needs of a growing refugee population. Deterrence objectives and criminalization of vulnerable foreigners should not overshadow welfare considerations when men, women and children are suffering in our community. As long as work rights are denied, the authorities have a legal and moral obligation to increase welfare to realistic levels consistent with human right laws.

Is the government promoting “no welfare – no work” entrapment?
Apr 20th, 2015 | Crime, Detention, Immigration, VF Opinion, Welfare | Comment
Called to the stand in Shatin Magistracy, Mohammed faced charges of breaching conditions of stay by taking up employment unlawfully. With the assistance of a Hindi interpreter, the despairing 50 year-old listened carefully before entering a plea – NOT GUILTY!
Asylum seekers are most commonly tarred with one brush. Public opinion is almost unanimous in accusing them of beating a path to our city to fraudulently drink in its riches by abusing welfare assistance, or toiling in the underground economy. Obfuscating the truth, the authorities regularly promote to the inattentive a rejection rate of 99.9% as evidence that only 1 in 1000 claims is meritorious.
The government remains unyielding and is adamant that the asylum mechanism offers genuine claimants a fair chance. No explanation is given about cases that have been pending for years often stretching to a decade. At the other end of the spectrum are recent arrivals who presumably didn’t expect to suffer like beggars after lodging protection claims with the Hong Kong Government.
Everything was better in Mohammed’s life before he took refuge in our city. If he didn’t face danger, he wouldn’t have left behind a supportive wife and adult children, abandoning a comfortable home and a thriving family business. At half a century of age, he hardly fits the stereotype of an adventurer seeking a better life in a developed country where illegal work might support remittances home.
One night, a few months after being released from Immigration detention, Mohammed regained consciousness in a ward at Queen Elizabeth Hospital. “I didn’t know how I got there. I was feeling ill that morning as I hadn’t had anything to eat and I was exhausted by sleeping outside week after week. The nurse told me that I had hit my head when I collapsed in the street. An ambulance was called and I was admitted to hospital for three days until I recovered.”
Holding back tears, he finds it hard to continue, “Those were the only three days when I ate properly since I was released from CIC. The nurses gave me extra food to make me stronger. For several months before I only ate what shops donated to me in Chung King Mansions. It was never enough. I lost a lot of weight and was often sick. I was worried when discharged from hospital as I knew I would be hungry.”
Mohammed reported that he had registered at the Social Welfare Department and had been referred to ISS-HK, but nobody called him for months. He forgets how long it was because several months passed in a blur of destitution, begging for handouts, sleeping in the streets, falling sick and depressed and always struggling with hunger. As if life couldn’t get more distressing, it did.
One Ramadan afternoon before the Zuhr prayers, he was accosted by a faithful at the Kowloon mosque who, presumably noticing his grime state, inquired about his condition. Mohammed explained that he was a refugee and had long run out of money and support. The well-wisher showed concern and with the enticement of a ‘breaking fast meal’ invited him on a trip in a private car to a recycling yard in Lok Ma Chau. The arrangement did not raise the suspicions of a newcomer in an international city.
Beggars can’t be choosers and nothing seemed out of the ordinary for hungry Mohammed about Muslim faithful offering desperately needed support in the name of Zakat – charity being one of the five pillars of Islam and a special obligation during Ramadan. Nobody suspected that police commandos were concealed in nearby bushes cocking machine guns to raid the isolated yard.
Around 3:30pm, before Mohammed enjoyed a single morsel of food, armed police burst inside. In the ensuing chaos, the panic-stricken refugee dove inside a wrecked car hugging the rusty floor until he was dragged out by the collar of his jacket two hours later, sweaty and confused. The fact that he was hiding from enforcement agents was subsequently put forward as evidence of his guilt.
Mohammed stands accused of working illegally. The police took photos of those arrested after the raid, not when they were allegedly working. The threadbare clothes of a homeless existence were put forward as work clothes, though Mohammed had arrived an hour earlier and his hands were clean.
It is certainly possible that Mohammed is lying and had accepted an offer for work at a time of acute desperation. Perhaps Mohammed is afraid of admitting the truth for fear of being jailed for 15 months for working illegally. Perhaps it wasn’t the first time he went to that yard and the police had failed to take such photo. But he claims to be innocent. And this arrest consequently raises more questions than answers.
How much of a crime is it to steal bread when you are hungry? How are refugees expected to survive for weeks and months before receiving welfare? For that matter, refugees are trapped between inadequate assistance and cope without breaking the law. Is the government promoting “no welfare – no work” entrapment? In some jurisdiction offenders may be found innocent when authorities use deception to make arrests. Shouldn’t the courts take note of contextual evidence?